"Should I take Menopause Hormone Therapy?"
This information is meant to help you understand:
That the research-based information below explains what tends to happen on average, not necessarily what will happen to/for you.
Where the benefits of MHT end and where the impact of training and nutrition begin.
Which parts of your body composition changes are due to aging vs. estrogen loss (menopause).
In other words, this is just research-based Please have a Convo with your doctor about your individual needs!
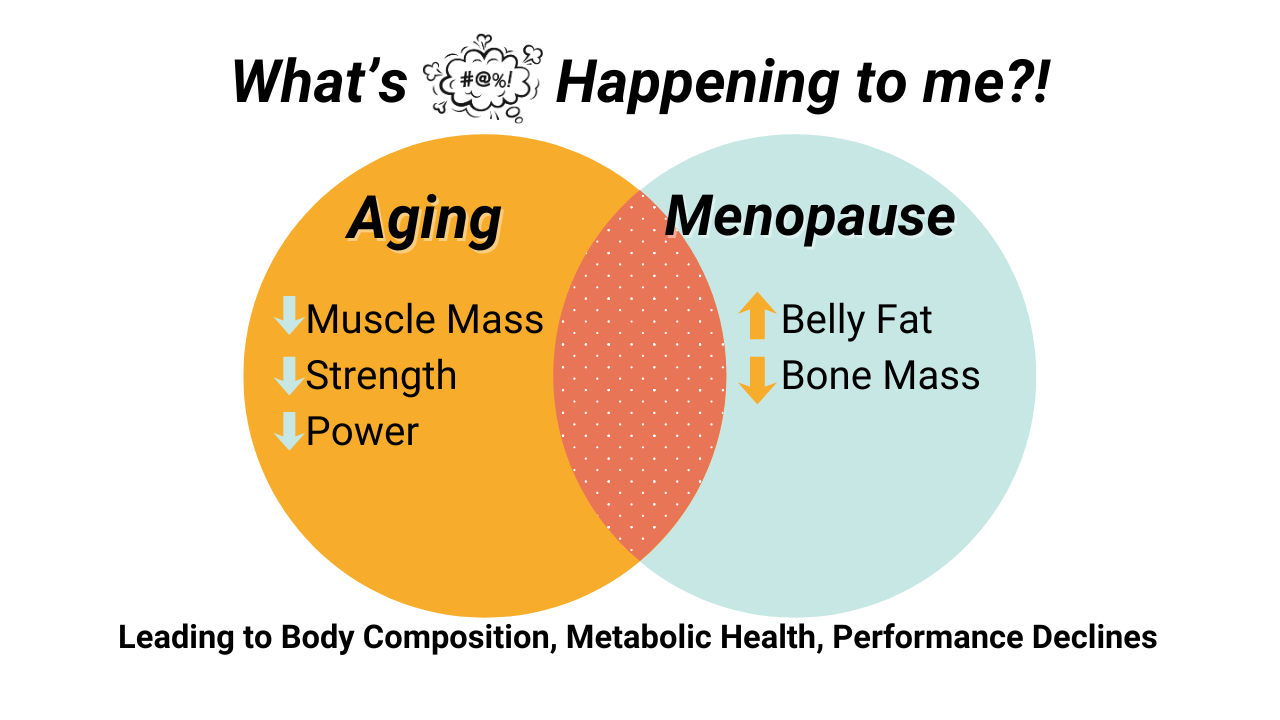
Aging vs. Menopause
Generally, aging is the mechanism for decline in muscle mass, strength, and power output, and for an increase in relative and absolute body fat.
Estrogen loss via Menopause is the cause for the change in fat accumulation location, plus muscle quality.
Estrogen loss is also directly responsible for bone mass decreases. MHT will minimally attenuate bone loss, and mechanical loading (lifting, jumping, etc.) is required for meanigfully maintaining bone.
We can also assume MHT mitigate the impact of the Musculoskeletal Syndrome of Menopause (low threshold for inflammation in any tissue but often tendons & joints, joint or general body pain/aches, arthritis onset,
MHT BENEFITS
Bio-identical Estrogen + Progesterone Manages Vasomotor Menopause Symptoms*
It also manages:
Muscle + tendon + joint aches and pain. Mitigates bone loss.
Genitourinary symptoms (dryness, UTIs, leaking, pain)
Mild anxiety & depression symptoms
Poor Sleep
*The official FDA-Approved indicators of prescribed use are 'Vasomotor and Genitourinary symptoms,' but can be prescribed for "off-label" symptoms as well. This means that you shouldn't have to tell your doc you experience hot flashes in order to get an Rx (but some women report they do).
Body Fat
Total body fat still tends to increase with age, regardless of MHT use. PMID: 24834015, PMID: 8440839
Visceral (between organs) : subcutaneous (pinchable under skin fat) ratio is lower in MHT users, decreasing associated health risks. PMID: 18332882, PMID: 7885283, PMID: 24834015
MHT doesn't prevent body fat increases, just the location of accumulation. PMID: 32219014
MHT Promotes Muscle Improvements
With strength training, MHT enhances or preserves gains, muscle quality, connective tissue, recovery, and response to training. (PMID: 33542694)
Women who use MHT and don't strength train lose muscle at about the same rate to women who neither use MHT nor strength train. In other words, MHT alone doesn’t preserve muscle. PMID: 31461147
Improves Health Biomarkers
Women who take MHT (vs. those who don't take MHT) have:
Lower A1C,
Lower Cholesterol Markers
Lower Fasting Glucose
Better insulin sensitivity
Lower Lp(a) -- genetically influenced indicator of heart attack or stroke
*Mode of estrogen replacement (oral vs. transdermal) and individual fat mass to fat free mass ratio inform the influence on these markers.
Mitigates Bone Loss
Estrogen promotes collagen & calcium formation and slows loss.
Prescription drugs taken for osteoporosis and osteopenia increase calcium content (the measurable part of a DEXA scan), but isn't able to restore/maintain the "willow tree-like" collagen content of a bone, so while these drugs can decrease breakdown, they also cause bones to become more brittle over time.
MHT RISKS
Vaginal bleeding
Estrogen + Progesterone therapies can cause breakthrough bleeding, especially in the first 6-12 months of use. PMID: 30495192
Prolonged or new-onset bleeding in women on MHT is not automatically dangerous, but biopsy is warranted to exclude pathology.
If you have a Mirena, it can help mitigate increased bleeding. PMID: 17531609
Breast cancer Risk
WIthout previous breast cancer: Combined estrogen + micronized progesterone (current standard) appears not increase breast cancer risk. Longer use still may carry some risk. PMID 35675607, PMID 27456847
With personal history of cancer: MHT is not considered safe or routine therapy after breast cancer occurrence because of evidence of possible increased recurrence risk and the lack of strong data showing safety in this group.
https://www.bcrf.org/about-breast-cancer/hrt-breast-cancer-risk/?utm_source=chatgpt.com
In BRCA1/BRCA2 gene carriers:
Observational data suggest no significant increase in breast cancer incidence with MHT use (including estrogen + progestogen) after surgical menopause (oophorectomy); estrogen‑alone regimens may even show reduced incidence in some studies. PMID: 41403285
Stroke & VTE
In healthy women who initiate menopausal hormone therapy before age 60 and/or within 10 years of menopause onset, major cardiovascular risk is not significantly elevated and may be lower overall, though some risks such as venous thromboembolism persist.
PMID: 25754617, 40488293
Hormone-Free Options:
Birth Control Pill
Combined Oral Contraceptives are effective for managing erratic cycles and heavy or unpredictable peri-menopausal bleeding. It may also manage night sweats and hot flashes in some people. It is not useful for other vasomotor symptoms. Some people develop other symptoms with this path (migraines, nausea).
It’s not designed to provide the same long-term health support that menopausal hormone therapy can.
PMIDs: 25534509, 41307293, 11521120, 11521120,
Anti-Depressants & Anti-Anxiety Drugs
Although antidepressants and anxiolytics are effective for treating mood disorders, they do not address the broader menopause-related physiological changes that menopausal hormone therapy can target, such as vasomotor symptoms, sleep disruption related to hot flashes, bone health, and genitourinary symptoms.
MHT is not an antidepressant.
But in menopause-related mood symptoms, it may play a supportive role.
PMIDs: 37603881, 25203891, 22132727